The Rise and Fall of the Rotary Engine
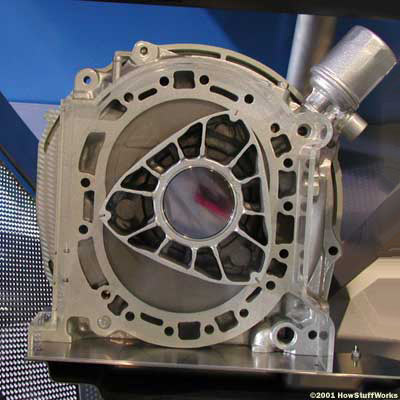
(Image via HowStuffWorks)
October 18, 2020
When you hear the word engine, what do you think of it? The average person probably would have pictured a block with a few pistons, but that is not always the case. In 1929 german engineer Felix Wankel invented the Wankel rotary engine. The engine was more simple and lighter than the internal combustion engine created only 57 years prior in 1872.
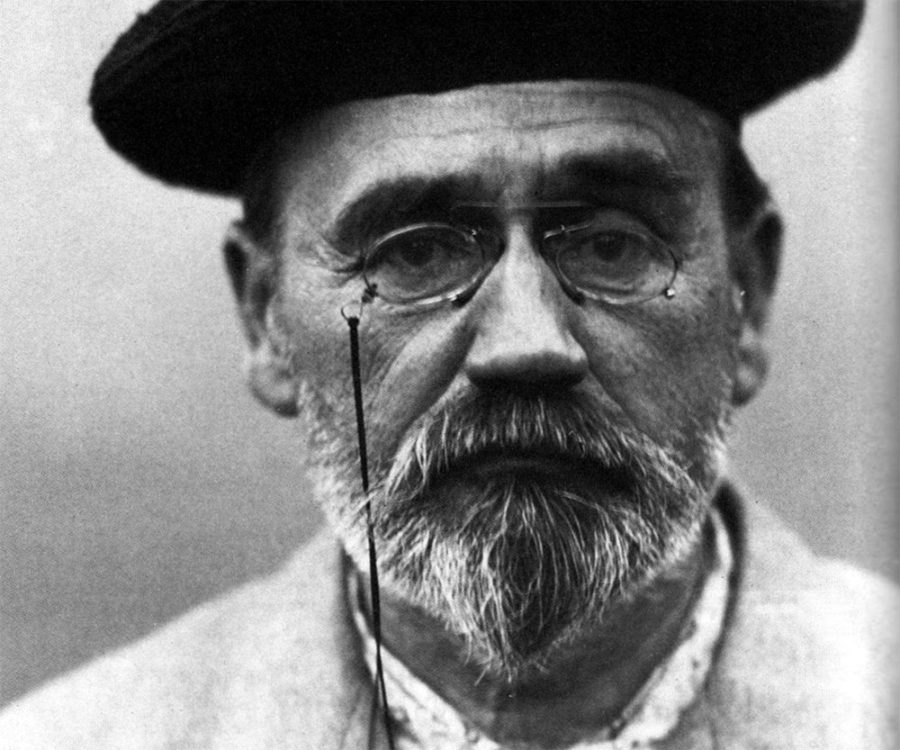
Who was Felix Wankel? Wankel was born on August 13th, 1902, and opened an unofficial machine shop in a shed with some friends. According to Wikipedia, it states that “One of his friends, who had graduated from university, gave his name and transformed the shop into an official garage for DKW and Cleveland Motor Bikes in 1927, where Wankel worked from time to time until his arrest in 1933.” Wankel invented his famous rotary engine at the age of 22 in 1924 but did not receive his first patent until 1929.
So how does it work? The oval-shaped engine block houses a triangular rotor. As the rotor cycles, it scoops and compresses the fuel then after two spark plugs ignite the air-fuel mixture forcing the rotor to trap the exhaust gases and throw them out the exhaust as it continues to rotate.
In 1963 Mazda released the first-ever mass-produced rotary-powered vehicle called the cosmo sport. This car was, “Designed right from the start to be driven by a rotary engine, the Cosmo Sport featured an unconventional styling that created a buzz.” according to Mazda. This was the only rotary-powered car until 1968 when Mazda released the Familia Rotary Coupe.
In 1970 the US passed the clean air act, which restricted the number of hydrocarbons released in exhaust gasses. Mazda’s rotary engine did not meet emissions standards until 1975. In 1978 Mazda released the rx7 which gained a high status after competing in and winning several races. In 1985 Mazda released the second-gen rx7, and in 1992 Mazda released its third and final generation of the rx7 before the suspension of the rotary engine due to an economic downturn in 2002.
In 2003 Mazda announced the return of the rotary in their newest model, the rx8. In 1995 they began working on a hydrogen-powered rotary in which was test fitted into an Mx-5 until 2003 when it was mass-produced in the rx8. According to Mazda, “ In 2006, Mazda became the world’s first company to launch practical use of a hydrogen rotary engine-powered car through a leasing arrangement.” The rx8 continued to be produced until 2011 when Mazda announced they would not be releasing a 2012 model, officially ending the production of Mazda rotary-powered cars.
For some time now, Mazda has been talking about the return of the rotary engine in 2022. They officially announced that the returned engine would be in the CX-30, a hybrid car that Mazda only recently began manufacturing. The vehicle has little resemblance to the RX series that the engine once powered, built to be an SUV rather than a sports car. Many are excited about the return of the rotary engine, but will the RX return with it?