The Fluidity of Halloween
October 18, 2020
Halloween or Hallowe’en, also known as Allhalloween, All Hallows’ Eve, or All Saints’ Eve, is a celebration observed in many countries on 31 October, the eve of the Western Christian feast of All Hallows’ Day. It begins the three-day observance of Allhallowtide, the time in the liturgical year dedicated to remembering the dead, including saints, martyrs, and all the faithful departed.
It is widely believed that many Halloween traditions originated from ancient Celtic harvest festivals, particularly the Gaelic festival Samhain that such festivals may have had pagan roots; and that Samhain itself was Christianized as Halloween by the early Church. Some believe, however, that Halloween began solely as a Christian holiday, separate from ancient festivals like Samhain.
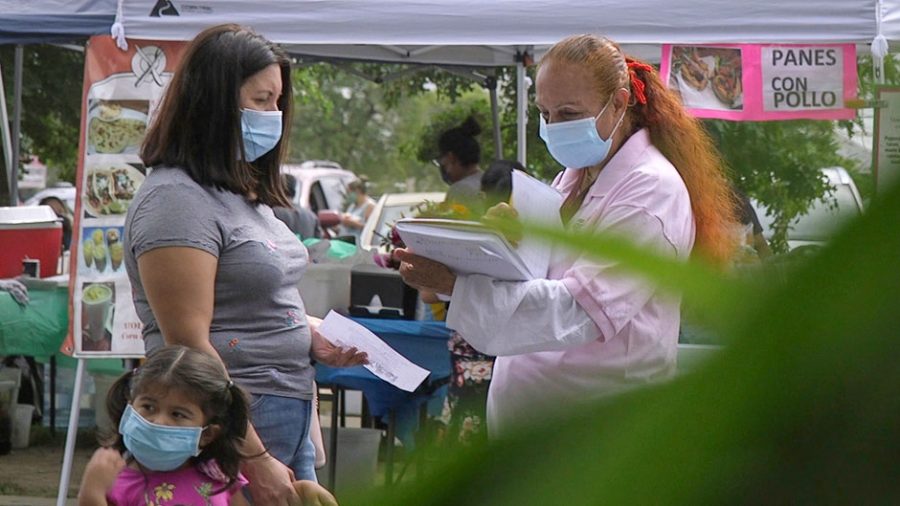
Halloween activities include trick-or-treating, attending Halloween costume parties, carving pumpkins into jack-o’-lanterns, and lighting bonfires. Others include apple bobbing, divination games, playing pranks, visiting haunted attractions, telling scary stories, and watching horror films. In many parts of the world, the Christian religious observances of All Hallows’ Eve include attending church services and lighting candles on the graves of the dead, remain popular, although elsewhere it is a more commercial and secular celebration. Some Christians historically abstained from meat on All Hallows’ Eve, a tradition reflected in the eating of certain vegetarian foods on this vigil day, including apples, potato pancakes, and soul cakes. The word Halloween or Hallowe’en dates to about 1745 and is of Christian origin. The word “Hallowe’en” means “Saints’ evening”. It comes from a Scottish term for All Hallows’ Eve.
Today’s Halloween customs are thought to have been influenced by folk customs and beliefs from the Celtic-speaking countries, some of which are believed to have pagan roots. Jack Santino, a folklorist, writes that “there was throughout Ireland an uneasy truce existing between customs and beliefs associated with Christianity and those associated with religions that were Irish before Christianity arrived”. Historian Nicholas Rogers, exploring the origins of Halloween, notes that while “some folklorists have detected its origins in the Roman feast of Pomona, the goddess of fruits and seeds, or in the festival of the dead called Parentalia, it is more typically linked to the Celtic festival of Samhain, which comes from the Old Irish for ‘summer’s end’.”
Samhain was the first and most important of the four quarter days in the medieval Gaelic calendar and was celebrated on 31 October – 1 November in Ireland, Scotland, and the Isle of Man. A kindred festival was held at the same time of year by the Brittonic Celts, called Calan Gaeaf in Wales, Kalan Gwav in Cornwall, and Kalan Goañv in Brittany; a name meaning “first day of winter”. For the Celts, the day ended and began at sunset; thus the festival began on the evening before 7 November by modern reckoning. Samhain and Calan Gaeaf are mentioned in some of the earliest Irish and Welsh literature. The names have been used by historians to refer to Celtic Halloween customs up until the 19th century, and are still the Gaelic and Welsh names for Halloween.
Samhain/Calan Gaeaf marked the end of the harvest season and beginning of winter or the ‘darker half’ of the year. Like Beltane/Calan Mai, it was seen as a liminal time, when the boundary between this world and the Otherworld thinned. This meant the Aos Sí, the ‘spirits’ or ‘fairies’, could more easily come into this world and were particularly active. Most scholars see the Aos Sí as “degraded versions of ancient gods whose power remained active in the people’s minds even after they had been officially replaced by later religious beliefs”. The Aos Sí were both respected and feared, with individuals often invoking the protection of God when approaching their dwellings. At Samhain, it was believed that the Aos Sí needed to be propitiated to ensure that the people and their livestock survived the winter. Offerings of food and drink, or portions of the crops, were left outside for the Aos Sí. The souls of the dead were also said to revisit their homes seeking hospitality. Places were set at the dinner table and by the fire to welcome them. The belief that the souls of the dead return home on one night of the year and must be appeased seems to have ancient origins and is found in many cultures throughout the world.